How Siding Materials Vary by Region and Climate sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with a casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we delve into the intricacies of siding materials and their regional adaptability, a fascinating world of construction choices unfolds, influenced by diverse climate considerations.
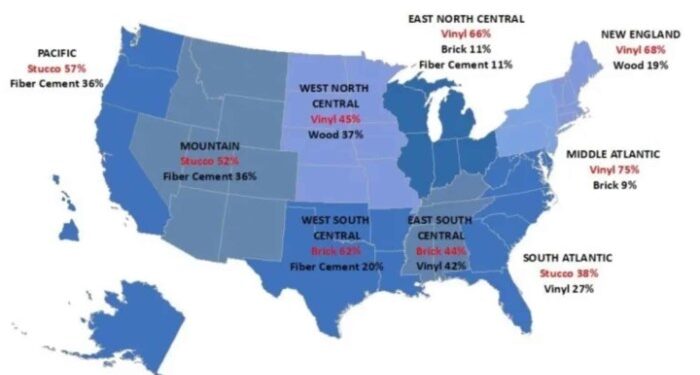
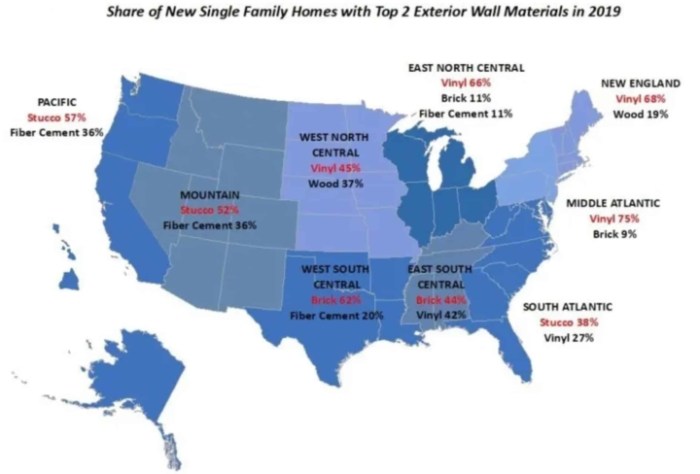
Materials Used for Siding

When it comes to siding materials, different regions around the world often rely on specific options that are best suited to their climate conditions. The choice of siding material plays a crucial role in the durability and longevity of a building's exterior.
Common Siding Materials by Region
In coastal areas or regions with high humidity levels, materials like vinyl and fiber cement are popular choices due to their resistance to moisture and salt exposure. Wood siding is commonly used in areas with moderate climates, as it provides a natural and aesthetically pleasing look.
In regions prone to wildfires, metal siding is often preferred for its fire-resistant properties.
Durability Based on Climate Variations
The durability of siding materials is heavily influenced by the climate of a particular region. For example, vinyl siding tends to crack in extreme cold temperatures, making it less suitable for regions with harsh winters. On the other hand, fiber cement siding is known for its durability in a variety of climates, including areas with high humidity and temperature fluctuations.
Influence of Regional Climate Factors
Regional climate factors such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation levels play a significant role in determining the ideal siding material for a specific area. For instance, areas with heavy rainfall may benefit from materials like brick or stone that can withstand moisture without deteriorating.
In regions with intense sun exposure, materials like stucco or metal siding are preferred for their ability to reflect heat and UV rays.
Wood Siding Varieties
Wood siding is a popular choice for homeowners due to its natural beauty and versatility. Different types of wood siding are preferred in various climates, each offering unique characteristics that cater to specific environmental conditions.
Types of Wood Siding
- Cedar Siding: Cedar is a popular choice for siding in humid climates due to its natural resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage.
- Pine Siding: Pine siding is commonly used in regions with more moderate climates, offering a cost-effective option with a warm, natural look.
- Redwood Siding: Redwood siding is known for its durability and resistance to rot, making it a preferred choice in areas with high moisture content.
Maintenance Requirements
Wood siding requires regular maintenance to ensure longevity and performance, with maintenance needs varying based on the climate of the region. In humid climates, wood siding may need more frequent painting or staining to prevent moisture damage and mold growth.
In dry climates, wood siding may require more frequent sealing to prevent cracking and warping due to the lack of moisture in the air.
Performance in Different Climates
Wood siding performs differently in humid versus dry climates. In humid climates, wood siding may be more prone to rot and mold growth if not properly maintained. In contrast, in dry climates, wood siding may be more susceptible to cracking and splitting due to the lack of moisture.
Proper installation and maintenance are key to ensuring the longevity and performance of wood siding in any climate.
Vinyl Siding Adaptations
Vinyl siding is a popular choice for homeowners in various regions due to its durability and low maintenance requirements. When it comes to extreme weather conditions, vinyl siding has been adapted to withstand these challenges effectively.One key adaptation for vinyl siding in extreme weather conditions is the inclusion of impact-resistant materials
This helps the siding withstand hail, strong winds, and other elements that may cause damage. Additionally, vinyl siding is designed to expand and contract with temperature changes, reducing the risk of cracking or warping.
Color Options for Vinyl Siding and Energy Efficiency
When it comes to energy efficiency, the color of vinyl siding plays a crucial role. Lighter colors tend to reflect heat, keeping homes cooler in warmer climates. On the other hand, darker colors absorb heat, making them suitable for colder regions where additional warmth is desired.
Homeowners can choose from a wide range of colors to suit their climate and energy efficiency needs.
Regions Where Vinyl Siding is Commonly Used
Vinyl siding is most commonly used in regions with extreme weather conditions, such as the Midwest and Northeast in the United States. These areas experience a wide range of temperatures throughout the year, making vinyl siding a practical choice due to its ability to adapt to different climates.
Additionally, coastal regions with high humidity levels often opt for vinyl siding due to its resistance to moisture and salt air corrosion.
Fiber Cement Siding Features
Fiber cement siding is a popular choice for homeowners in regions with specific weather patterns due to its durability and resistance to harsh conditions. This siding material is known for its low maintenance requirements and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and moisture levels.
Advantages of Fiber Cement Siding in Specific Weather Patterns
- Resistant to moisture: Fiber cement siding is ideal for regions with high humidity or frequent rain, as it does not rot or warp like wood siding.
- Temperature resilience: In areas with fluctuating temperatures, fiber cement siding remains stable and does not expand or contract, reducing the risk of cracks or damage.
- Fire resistance: Fiber cement siding is non-combustible, making it a safe choice for regions prone to wildfires or other fire hazards.
Installation Challenges of Fiber Cement Siding in Different Climates
- Cold climates: In colder regions, the installation of fiber cement siding can be challenging due to the risk of cracking during the curing process in low temperatures.
- Humid climates: High humidity levels can prolong the drying time of fiber cement siding, leading to potential issues with adhesion and overall installation quality.
- Extreme heat: In regions with intense heat, special care must be taken during installation to prevent warping or distortion of the siding panels.
Cost-Effectiveness of Fiber Cement Siding in Various Geographic Locations
- Initial cost: While fiber cement siding may have a higher upfront cost compared to other materials, its durability and low maintenance requirements can result in long-term cost savings for homeowners in all geographic locations.
- Climate impact: In regions with harsh weather conditions, the cost-effectiveness of fiber cement siding shines through as it requires minimal repairs and replacements over time, reducing overall expenses.
- Return on investment: Homeowners in areas prone to weather-related damage may see a higher return on investment with fiber cement siding due to its ability to withstand the elements and maintain its appearance for years to come.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the exploration of how siding materials vary by region and climate illuminates the dynamic interplay between construction materials and environmental factors, showcasing the nuanced decisions made in the realm of architecture and design.
Popular Questions
How do regional climate factors influence material choices for siding?
Regional climate factors play a crucial role in determining the durability, maintenance requirements, and performance of siding materials in different areas. For example, wood siding might be preferred in humid regions for its natural resistance to moisture, while vinyl siding with color options suited for energy efficiency might be more common in extreme climates.
What are the key advantages of fiber cement siding in regions with specific weather patterns?
Fiber cement siding offers excellent durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions like extreme heat or cold. Its installation challenges vary depending on the climate, but its cost-effectiveness makes it a popular choice in various geographic locations.
How does wood siding perform differently in humid versus dry climates?
Wood siding may expand and contract more in humid climates due to moisture absorption, requiring more maintenance to prevent rot or decay. In dry climates, wood siding might be less prone to these issues but could face challenges related to cracking or splitting.